ASP.NET Core 6: Bring your custom compression provider in gRPC
Introduction
The compression of data during their transport on the Internet or a network makes it possible to gain significantly in terms of performance. If gRPC is already efficient thanks to the payloads transported in binary via HTTP/2, it is possible to improve its performance a little more. It is possible to use Gzip compression quite easily with gRPC, however if you plan to use another compression algorithm, such as Brotli, you will have to implement it yourself and that is what I will show you in this article.
Implementing Brotli compression provider
Implementing a compression provider for gRPC requires inheriting from a specific interface: ICompressionProvider. This interface is in the Grpc.Net.Compression namespace and has two functions and one property:
This element being identified we can now implement our compression class. We will use Brotli as the compression provider. to do this, we will rely on the BrotliStream class, belonging to the System.IO.Compression namespace. Then we can implement our compression function, decompression and define the name of our encoder. They are here about “br” which defines the use of Brotli as compression algorithm in the headers, “grpc-accept-encoding” more exactly:
That’s pretty straightforward as you can see.
Enabling Brotli compression on gRPC
As you can imagine, for the compression to work, the client must be setup to compress and decompress the messages sent and received to/from the server. Same thing on the server side of course. Let’s start with the server:
You may have noticed CompressionProviders option takes a list of compression provider. It’s means you can implement several compression algorithm on your server, and, depending on what the client is requesting, the server can select the right compression to apply. This is driven by the “grpc-accept-encoding” sent by the client.
Client-side it’s simpler you simply need to enable Brotli like this:
Obvisouly, there is no magical there, both side needs to reference the compression provider implementation (if you are implementing both).
That’s it! Since the client enables Brotli compression, it will use it automatically.
Demo
After creating a client and a server gRPC app and you enable Brotli you should now see in the log (server-side) the following when the server send the response to the client:
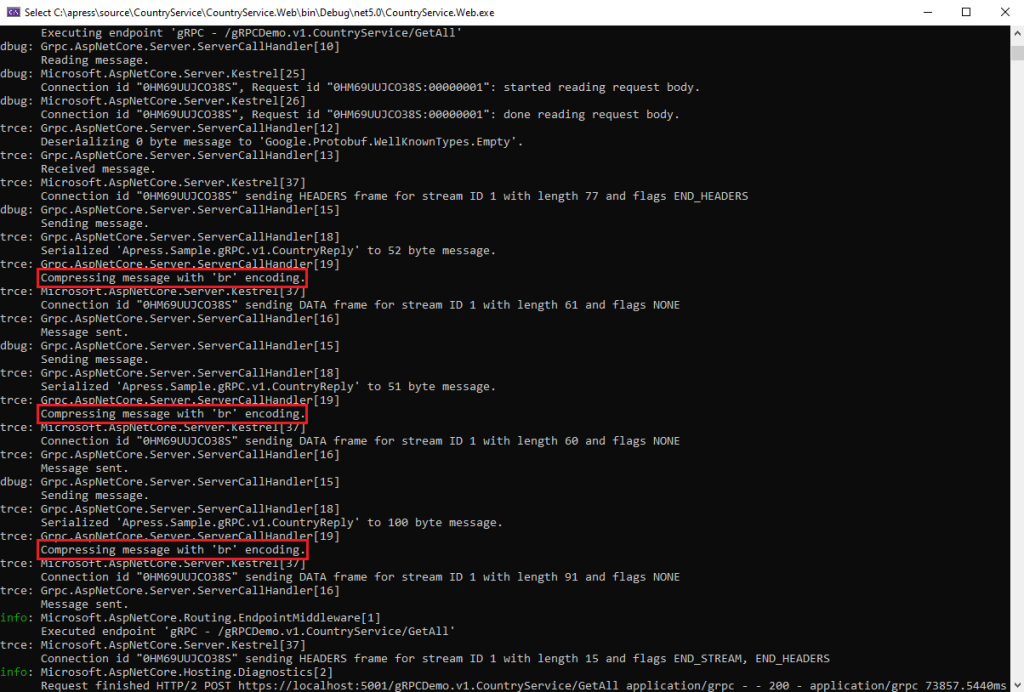
And client-side since it receives the response from the server:
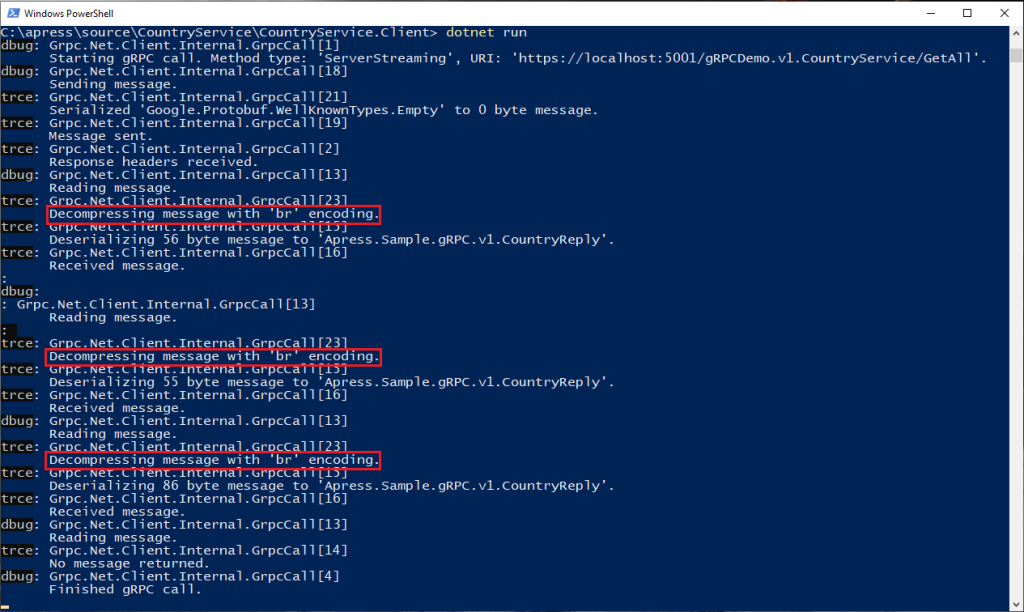
Easy isn’t it ? 🙂