gRPC & ASP.NET Core 3.1: Message validation
Introduction
Validation is a very important feature in applications but in ASP.NET Core 3.1 and gRPC it’s a bit complicated…. Proto3 doesn’t provide any validation with its syntax and Microsoft gaves us the habit to use DataAnnotation in ASP.NET and ASP.NET Core, unfortunaltey this feature is not available neither in gRPC. So a solution is required to fix that limitation, in this article I will show you how to use packages I have designed : Calzolari.Grpc.AspNetCore.Validation and Calzolari.Grpc.Net.Client.Validation. The full documentation is available here: https://github.com/AnthonyGiretti/grpc-aspnetcore-validator (forked and improved with more features from https://github.com/enif-lee/grpc-dotnet-validator).
Validation server side
First we’ll need to download the server side package with the following command:
Install-Package Calzolari.Grpc.AspNetCore.Validation -Version 3.1.2
The package is based on FluentValidation, if you want to learn more about it here is the link of their great documentation: https://docs.fluentvalidation.net/en/latest/
Now let’s consider the following service:
It’s a creation operation so we need to implement a validation on CountryCreateRequest parameter which is the message defined in the Proto3 file:
We need to make mandatory the “Name” and “Description” properties, and based on FluentValidation documentation the validator to write should look like this:
Once done, we will add three intructions in our Startup.cs:
- Enable message validation with EnableMessageValidation() extension on gRPC options.
- Configure validation with AddGrpcValidation() extension on services.
- And finally add our custom validator with FluentValidation extension AddValidator() on services.
Our Startup.cs should look like this:
The gRPC service is now well configured, now we can write the client and consume our service.
If you are using Blazor WebAssembly client-side, don’t forget to setup CORS rules with the following headers server-side:
.WithExposedHeaders("Grpc-Status", "Grpc-Message", "Grpc-Encoding", "Grpc-Accept-Encoding", "validation-errors-text");
Catching validation errors client side
To be able to read error validation messages we need to install the following package:
Install-Package Calzolari.Grpc.Net.Client.Validation -Version 3.1.2
Now let’s write our client, miss the “Description” property and add an extension on RpcException named GetValidationErrors() in our catch block.
The client should look like this:
Now let’s try!
Demo
Let’s execute and see how errors look like:
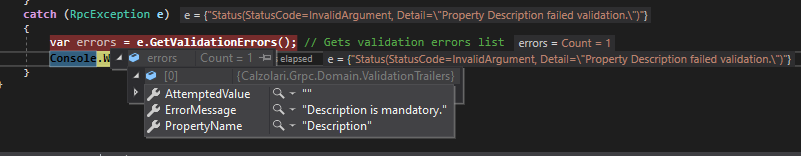
Actually the library return 3 metadata
- The value passed to the service
- The error message
- The involved property name
So how do you like it? 🙂
If you have any suggestion to make the library more powerful just let me know 😉